

From the moment the COVID-19 pandemic was declared in March 2020, our teams at Lawson Health Research Institute have been at the forefront. Researchers at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London immediately began to work towards understanding the new virus in an effort to discover lifesaving health-care solutions.
To date, dozens of research projects have been advanced through Lawson with some receiving international attention as ‘world firsts’. As we mark the three-year anniversary of COVID-19 being declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO), we share with you COVID-19 research highlighted over the past year.
Study finds acute kidney injury associated with severe COVID-19 leads to high mortality rates
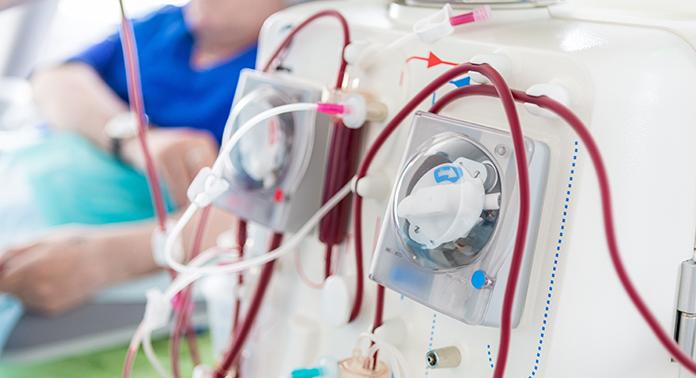
Severe cases of a COVID-19 infection can cause a host of serious complications, including acute kidney injury. In a published study, scientists at Lawson found that acute kidney injury in patients with a severe COVID-19 infection leads to a high mortality rate.
By accessing data collected through the Ontario Renal Network (ORN), Dr. Peter Blake, Lawson Researcher and Provincial Medical Director at the Ontario Renal Network, and his colleagues examined 271 people at 27 renal programs across the province, including patients at LHSC, who received dialysis for acute kidney injury due to a COVID-19 infection. Read more.
Study shows a decline in Veterans’ mental health throughout the pandemic

In published findings from Lawson, more than half of Canadian Veterans reported a decline in their mental health over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic.
When it comes to mental health conditions, Veterans are an at-risk population, often having higher rates of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, scientists at Lawson wanted to understand its effects on this already at-risk population.
To examine the potential impacts the research team launched a longitudinal study recruiting Canadian Veterans and spouses of Canadian Veterans. Participants complete online questionnaires every three months, with questions focused on mental health and virtual health care services. Read more.
Virtual care associated with significant environmental and patient cost savings

A study published in JAMA Network Open by researchers at ICES, Lawson and Western University found that virtual care during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a significant reduction in carbon dioxide emissions and patient travel-related expenses, such as gasoline, parking or public transit costs.
Findings show that for more than 10 million patients with at least one appointment during the study period (63 million visits in total), virtual care was associated with estimated savings of:
• 3.2 billion kilometers of patient travel;
• 545 to 658 million kilograms of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions; and
• $569 to $733 million (Canadian [US $465-$599 million]) in expenses for gasoline, parking, or public transit. Read more.
London researchers discover novel method to diagnose long COVID

Published in Molecular Medicine, researchers at Lawson found that patients with post-COVID-19 condition (long COVID) have unique biomarkers in their blood. The team is now working on developing a first of its kind blood test that could be used to diagnose long COVID. The discovery could also lead to new therapeutics for this condition.
The researchers studied 140 blood samples from participants at LHSC and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, including St. Joseph’s Post-Acute COVID-19 Program. Participants were those with presumed long COVID, hospital inpatients with acute COVID-19 infection and healthy control subjects. Read more.
Researchers are combining new technologies to examine blood proteins in COVID-19 patients

Published in the Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, a team at Lawson discovered unique patterns of blood plasma proteins in critically ill patients that may help develop a more personalized approach to treating severe COVID-19.
Called the plasma proteome, the proteins studied are released by cells that often play an important role in the body’s immune response to viruses. The research team studied how they adapt and change to a COVID-19 infection. Read more.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca